Relationship Field
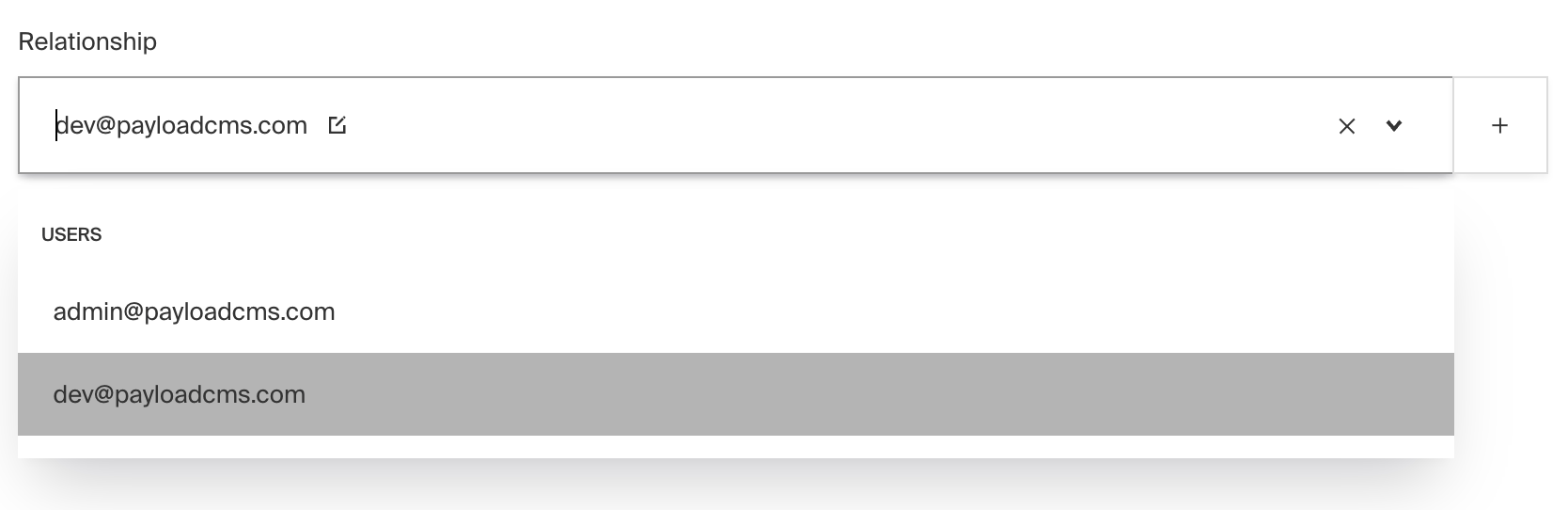
Example uses:
- To add
Productdocuments to anOrderdocument - To allow for an
Orderto feature aplacedByrelationship to either anOrganizationorUsercollection - To assign
Categorydocuments toPostdocuments
Config
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
name * | To be used as the property name when stored and retrieved from the database. More |
relationTo * | Provide one or many collection slugs to be able to assign relationships to. |
filterOptions | A query to filter which options appear in the UI and validate against. More. |
hasMany | Boolean when, if set to true, allows this field to have many relations instead of only one. |
minRows | A number for the fewest allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with hasMany. |
maxRows | A number for the most allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with hasMany. |
maxDepth | Sets a number limit on iterations of related documents to populate when queried. Depth |
label | Text used as a field label in the Admin panel or an object with keys for each language. |
unique | Enforce that each entry in the Collection has a unique value for this field. |
validate | Provide a custom validation function that will be executed on both the Admin panel and the backend. More |
index | Build an index for this field to produce faster queries. Set this field to true if your users will perform queries on this field's data often. |
saveToJWT | If this field is top-level and nested in a config supporting Authentication, include its data in the user JWT. |
hooks | Provide field-based hooks to control logic for this field. More |
access | Provide field-based access control to denote what users can see and do with this field's data. More |
hidden | Restrict this field's visibility from all APIs entirely. Will still be saved to the database, but will not appear in any API or the Admin panel. |
defaultValue | Provide data to be used for this field's default value. More |
localized | Enable localization for this field. Requires localization to be enabled in the Base config. |
required | Require this field to have a value. |
admin | Admin-specific configuration. See the default field admin config for more details. |
custom | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
* An asterisk denotes that a property is required.
Admin config
In addition to the default field admin config, the Relationship field type also allows for the following admin-specific properties:
isSortable
Set to true if you'd like this field to be sortable within the Admin UI using drag and drop (only works when hasMany
is set to true).
allowCreate
Set to false if you'd like to disable the ability to create new documents from within the relationship field (hides
the "Add new" button in the admin UI).
sortOptions
The sortOptions property allows you to define a default sorting order for the options within a Relationship field's
dropdown. This can be particularly useful for ensuring that the most relevant options are presented first to the user.
You can specify sortOptions in two ways:
As a string:
Provide a string to define a global default sort field for all relationship field dropdowns across different collections. You can prefix the field name with a minus symbol ("-") to sort in descending order.
Example:
This configuration will sort all relationship field dropdowns by "fieldName" in ascending order.
As an object :
Specify an object where keys are collection slugs and values are strings representing the field names to sort by. This allows for different sorting fields for each collection's relationship dropdown.
Example:
In this configuration:
- Dropdowns related to
pageswill be sorted by"fieldName1"in ascending order. - Dropdowns for
postswill use"fieldName2"for sorting in descending order (noted by the "-" prefix). - Dropdowns associated with
categorieswill sort based on"fieldName3"in ascending order.
Note: If sortOptions is not defined, the default sorting behavior of the Relationship field dropdown will be used.
Filtering relationship options
Options can be dynamically limited by supplying a query constraint, which will be used both for validating input and filtering available relationships in the UI.
The filterOptions property can either be a Where query, or a function returning true to not filter, false to
prevent all, or a Where query. When using a function, it will be
called with an argument object with the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
relationTo | The relationTo to filter against (as defined on the field) |
data | An object of the full collection or global document currently being edited |
siblingData | An object of the document data limited to fields within the same parent to the field |
id | The value of the collection id, will be undefined on create request |
user | The currently authenticated user object |
Example
You can learn more about writing queries here.
How the data is saved
Given the variety of options possible within the relationship field type, the shape of the data needed for creating
and updating these fields can vary. The following sections will describe the variety of data shapes that can arise from
this field.
Has One
The most simple pattern of a relationship is to use hasMany: false with a relationTo that allows for only one type
of collection.
The shape of the data to save for a document with the field configured this way would be:
When querying documents in this collection via REST API, you could query as follows:
?where[owner][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024.
Has One - Polymorphic
Also known as dynamic references, in this configuration, the relationTo field is an array of Collection slugs that
tells Payload which Collections are valid to reference.
The shape of the data to save for a document with more than one relationship type would be:
Here is an example for how to query documents by this data (note the difference in referencing the owner.value):
?where[owner.value][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024.
You can also query for documents where a field has a relationship to a specific Collection:
?where[owners.relationTo][equals]=organizations.
This query would return only documents that have an owner relationship to organizations.
Has Many
The hasMany tells Payload that there may be more than one collection saved to the field.
To save the to hasMany relationship field we need to send an array of IDs:
When querying documents, the format does not change for arrays:
?where[owners][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024.
Has Many - Polymorphic
Relationship fields with hasMany set to more than one kind of collections save their data as an array of objects—each
containing the Collection slug as the relationTo value, and the related document id for the value:
Querying is done in the same way as the earlier Polymorphic example:
?where[owners.value][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024.
Querying and Filtering Polymorphic Relationships
Polymorphic and non-polymorphic relationships must be queried differently because of how the related data is stored and
may be inconsistent across different collections. Because of this, filtering polymorphic relationship fields from the
Collection List admin UI is limited to the id value.
For a polymorphic relationship, the response will always be an array of objects. Each object will contain
the relationTo and value properties.
The data can be queried by the related document ID:
?where[field.value][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024.
Or by the related document Collection slug:
?where[field.relationTo][equals]=your-collection-slug.
However, you cannot query on any field values within the related document. Since we are referencing multiple collections, the field you are querying on may not exist and break the query.